Fire Eel: Comprehensive Care Guide, Facts, and Habitat
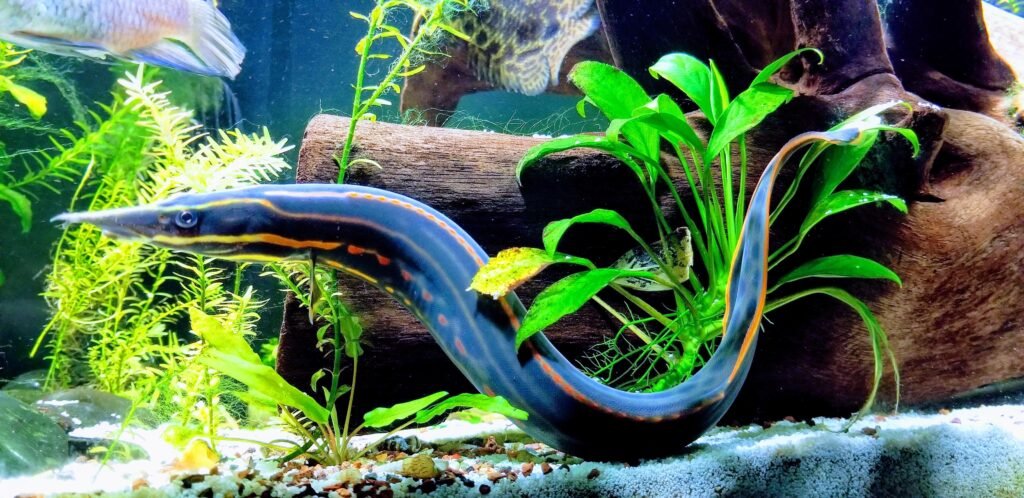

Fire Eel: Comprehensive Care Guide, Facts, and Habitat
Discover the Unique Fire Eel: A Complete Care Guide and Fascinating Facts
Introduction
The Fire Eel (Mastacembelus erythrotaenia) is a striking and unique species known for its elongated body and vibrant coloration. Native to the freshwater rivers of Southeast Asia, these eels are popular in the aquarium trade due to their distinctive appearance and intriguing behavior. Understanding the natural habitat, dietary needs, and care requirements of the Fire Eel is crucial for providing optimal conditions in captivity and ensuring their well-being.
These eels are characterized by their long, slender bodies adorned with bright red and yellow markings. They are nocturnal and prefer to stay hidden during the day, emerging at night to hunt for food. To thrive in captivity, Fire Eels require a well-maintained aquarium that mimics their natural environment, with plenty of hiding spots and a soft substrate.
Maintaining the right water parameters, such as a pH of 6.5-7.5 and a temperature of 75-82°F, is essential. Regular water changes and efficient filtration are crucial to keeping the water quality high. Feeding these eels a diet rich in protein helps keep them healthy and vibrant.
Facts
| Fact | Detail |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Mastacembelus erythrotaenia |
| Common Names | Fire Eel, Fire Spiny Eel |
| Year Discovered | 1850 |
| Kingdom | Animalia |
| Phylum | Chordata |
| Class | Actinopterygii |
| Order | Synbranchiformes |
| Family | Mastacembelidae |
| Genus | Mastacembelus |
| Species | M. erythrotaenia |
| Max Size | Up to 40 inches |
| Temperament | Semi-aggressive |
| Aquarium Level | Bottom Level |
| Difficulty | Moderate to Advanced |
| Shoaling | Solitary |
| Best Kept As | Single specimen |
| Diet and Feeding | Carnivorous |
| Reproduction | Egg layers |
| Average Lifespan | 10-20 years |
Appearance
The Fire Eel is easily recognizable by its elongated body covered with bright red and yellow stripes and spots. These colors become more pronounced as the eel matures, making it a visually stunning addition to any aquarium.
Distribution
Fire Eels are native to Southeast Asia, particularly in the river basins of Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia, and Vietnam. They inhabit slow-moving rivers, streams, and flooded areas with dense vegetation.
Habits and Lifestyle
Fire Eels are nocturnal and spend most of the day hidden among the substrate or under decorations in the aquarium. They are active hunters at night, preying on small fish, invertebrates, and worms. These eels are known for their burrowing behavior, so a soft substrate is recommended to prevent injury.
Care Guide
Tank Setup: A tank of at least 75 gallons is recommended, with plenty of hiding spots such as rocks, driftwood, and PVC pipes. A soft substrate like sand is ideal for burrowing.
Water Parameters: Fire Eels thrive in water with a pH of 6.5-7.5 and a temperature of 75-82°F. Efficient filtration and regular water changes are crucial for maintaining water quality.
Diet: Feed a diet rich in protein, including live or frozen foods like earthworms, bloodworms, and shrimp. They may also accept high-quality carnivore pellets.
Physical Characteristics
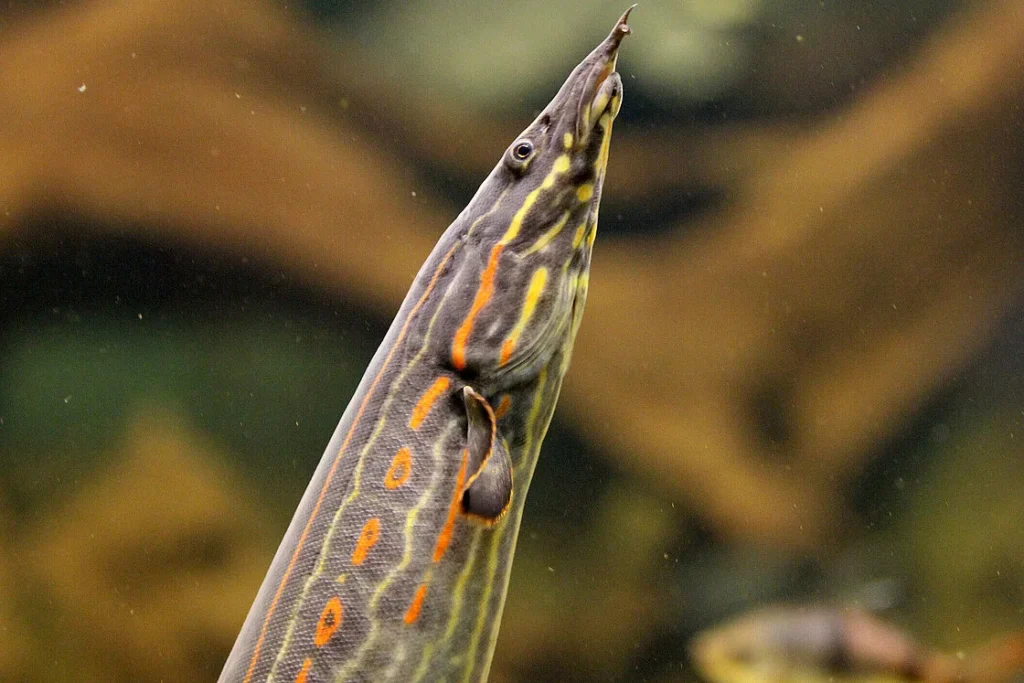

Fire Eels can grow up to 40 inches in length, although they are often smaller in captivity. They have a long, slender body with bright red and yellow markings that become more vibrant as they age.
Diet and Nutrition
These eels are carnivorous and thrive on a diet of live or frozen foods such as earthworms, bloodworms, and shrimp. Offering a variety of protein-rich foods helps ensure they receive balanced nutrition.
Breeding and Business
Breeding Fire Eels in captivity is challenging due to their specific environmental requirements and the need for precise water conditions. They are egg layers and require a separate breeding tank with optimal conditions.
Breeding Techniques: To breed Fire Eels, set up a breeding tank with plenty of hiding spots and soft substrate. The water should be clean and stable with a temperature around 80°F. After spawning, the eggs should be carefully monitored and the fry fed small live foods.
Health and Diseases
Fire Eels are generally hardy but can be susceptible to common freshwater diseases such as ich, bacterial infections, and parasites. Maintaining high water quality and a proper diet can help prevent these issues. Regular health checks and quarantine of new fish can also mitigate disease risks.
Common Diseases:
- Ich: Symptoms include white spots on the body and fins. Treat with elevated water temperatures and ich-specific medication.
- Bacterial Infections: Look for redness, ulcers, or fin rot. Antibiotic treatments in a quarantine tank are usually effective.
- Parasites: Symptoms include scratching against objects and rapid breathing. Anti-parasitic medications can help.
Commercial Medicines: Some commonly used medications for treating diseases in Fire Eels include:
- Ich Treatment: Malachite Green, Formalin
- Bacterial Infections: Maracyn, Kanamycin
- Parasites: Praziquantel, Metronidazole
Behavior
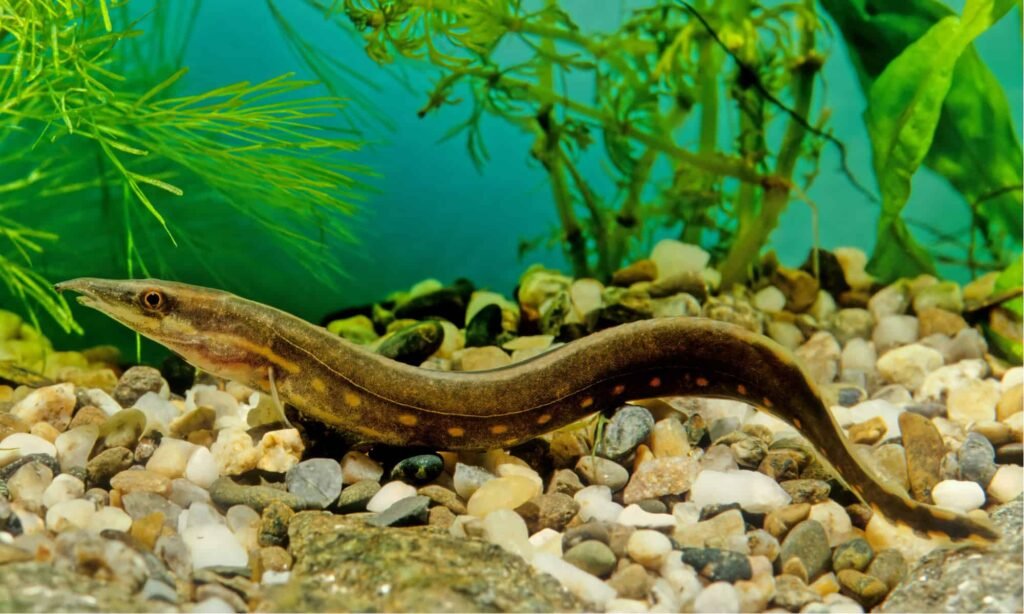

Fire Eels are generally semi-aggressive and may prey on smaller tank mates. They are best kept as single specimens due to their territorial nature. They exhibit interesting behaviors such as burrowing and active hunting at night.
FAQs
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| How big do Fire Eels get? | They can grow up to 40 inches in length. |
| What do they eat? | Their diet should consist of protein-rich foods such as earthworms, bloodworms, and shrimp. |
| Can they live with other fish? | They can be kept with larger, non-aggressive fish but may prey on smaller tank mates. |
| How do you breed Fire Eels? | Breeding is challenging and requires a separate breeding tank with optimal water conditions. They are egg layers and need a soft substrate for spawning. |
| What is the ideal tank setup? | A large tank with a soft substrate, plenty of hiding spots, a pH of 6.5-7.5, and a temperature of 75-82°F. |
Related Fish or Tank Mates
Suitable tank mates include other large, non-aggressive fish such as certain cichlids and large catfish. Avoid keeping them with small fish that may be seen as prey.
Price Table
| Region | Price (USD) | Date |
|---|---|---|
| North America | $30-$50 | June 2024 |
| Europe | €25-€45 | June 2024 |
| Asia | $20-$40 | June 2024 |
| Australia | AUD 35-55 | June 2024 |
Factors Affecting Price
- Rarity and demand
- Size and age of the fish
- Breeding and rearing conditions
- Transportation and import costs
References
Categories: Eels, Freshwater Fish, Tropical Fish, Aquarium Fish, Southeast Asian Fish, Predatory Fish, Bottom Dwellers
Views: 2